SPECIALTIES
- Home
- /
- Specialties
SUBURBAN ORTHOPAEDIC MEDICAL CENTER MAIN SERVICES
Suburban Orthopaedic Medical Center, in Newark, NJ, strives to provide the highest quality of care for our patients by combining multiple specialties, Chiropractic, Interventional Pain Management, Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Physical Therapy and Orthopedics, into one office. This approach allows our physicians to collaborate on our patients' conditions, and give them benefits of different treatment approaches.
DOCTORS OF CHIROPRACTIC (DC)
ABOUT DOCTORS OF CHIROPRACTIC
Suburban Orthopaedic Medical Center is the premier destination for those living and working in Newark, New Jersey and surrounding areas, for the ultimate patient experience in chiropractic care. This experience starts with our knowledgeable and caring staff. In partnership with our doctors, they provide the highest quality of chiropractic care and services. The doctors design individual treatment plans in order to meet the specific treatment goals of every patient.
We also have an extensive physical therapy department here for our patients’ convenience. Our team can provide core strengthening and electrical muscle stimulation and decompression in addition to chiropractic adjustments to help you achieve optimal health.

What is a Doctor of Chiropractic?
Doctors of chiropractic must complete four to five years at an accredited chiropractic college. The complete curriculum includes a minimum of 4,200 hours of classroom, laboratory and clinical experience. Approximately 555 hours are devoted to learning about adjustive techniques and spinal analysis in colleges of chiropractic.
In medical schools, training to become proficient in manipulation is generally not required of, or offered to, students. The Council on Chiropractic Education requires that students have 90 hours of undergraduate courses with science as the focus. Those intending to become doctors of chiropractic must also pass the national board exam and all exams required by the state in which the individual wishes to practice. The individual must also meet all individual state licensing requirements in order to become a doctor of chiropractic.
What it Takes to Become a Chiropractor
An individual studying to become a doctor of chiropractic receives an education in both the basic and clinical sciences and in related health subjects. The intention of the basic chiropractic curriculum is to provide an in-depth understanding of the structure and function of the human body in health and disease.
The educational program includes training in the basic medical sciences, including anatomy with human dissection, physiology, and biochemistry. Thorough training is also obtained in differential diagnosis, radiology and therapeutic techniques. This means, a doctor of chiropractic can both diagnose and treat patients, which separates them from non-physician status providers, like physical therapists. According to the Council on Chiropractic Education DCs are trained as Primary care Providers.
The proper title for a doctor of chiropractic is “doctor” as they are considered physicians under Medicare and in the overwhelming majority of states. The professional credentials abbreviation “D.C.” means doctor of chiropractic. ACA also advocates in its Policies on Public Health that DCs may be referred to as (chiropractic) physicians as well.
Chiropractic Philosophy
As a profession, the primary belief is in natural and conservative methods of health care. Doctors of chiropractic have a deep respect for the human body’s ability to heal itself without the use of surgery or medication. These doctors devote careful attention to the biomechanics, structure and function of the spine, its effects on the musculoskeletal and neurological systems, and the role played by the proper function of these systems in the preservation and restoration of health.
A Doctor of chiropractic is one who is involved in the treatment and prevention of disease, as well as the promotion of public health, and a wellness approach to patient healthcare.
Scope of Practice
Doctors of chiropractic frequently treat individuals with neuro-musculoskeletal complaints, such as headaches, joint pain, neck pain, low back pain and sciatica. Chiropractors also treat patients with osteoarthritis, spinal disk conditions, carpal tunnel syndrome, tendonitis, sprains, and strains. However, the scope of conditions that Doctors of chiropractic manage or provide care for is not limited to neuro-musculoskeletal disorders.
A variety of techniques, treatment and procedure are used to restore healing which will be the topic of future education releases.
SERVICE AREAS AND SYMPTOMS
 Call Today
Call Today
(973) 483-2277
Chiropractors are trained to help patients who suffer from pain related to very common situations, such as:
> Work Injuries
> Whiplash
> Sports Injuries
> Slips & Falls
> Work Injuries
Whatever the injury, chiropractors assist patients with a combination of “active” and “passive” care. Active care requires patient involvement (e.g., stretching, strengthening, biofeedback). Passive care involves treatment given to the patient (e.g., spinal manipulation, ultrasound, massage, medication).
Service that are provided by a chiropractor may include:
> Physical examination
> Chiropractic manipulation therapy (adjustments)
> Naprapathic plus various soft tissue therapies
> Physio therapeutic modalities
> Rehab exercise and stretching
> Orthopedic supports
> Nutritional counseling and supplements
> Consultation
COMMON MUSCULOSKELETAL CONDITIONS TREATED:
> Whiplash injury
> Sciatica and disc herniation
> Headaches and migraines
> Work, auto, and sport injuries
> Sprains and strains
> Arthritis
> Carpal tunnel syndrome
> Upper, mid or low back pain
> Neck Pain & Stiffness
> Shoulder Pain
> Numbness/Tingling
> Chest Pain
> Extremity Pain (Arm & Leg)
> Hip Pain
> Knee Pain
> Ankle/Foot Pain
> Disc Herniation
> Sciatica
> Muscle Spasm
> Pinched Nerve
> Tendonitis
> Stress
> Fibromyalgia
> Ear Aches
> Sprains/Strains
> Scoliosis
> Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
> Discomfort Caused by Pregnancy
> Arthritis
> TMJ Syndrome/Dysfunction
WHAT IS INTERVENTIONAL PAIN MANAGEMENT?
Interventional pain care patients at Suburban Orthopaedic Medical Center, in Newark New Jersey, are given a thorough evaluation to determine the source of their pain, and medically-responsible treatment plans are tailored for each patient. If medication is prescribed, patients are educated on its use and required to agree to strict guidelines.
This is a relatively new medical specialty that provides diagnosis and treatment to patients with all types of pain. The majority of patients referred to pain specialists are those whose pain has been stubborn and has failed to respond to the normal and standard medical treatments offered by their primary care physicians or other specialists (such as orthopedic surgeons, family practitioners, oncologists, etc.).
Patients with pain related to many common chronic or acute illnesses such as back pain, diabetes and other forms of nerve injuries, cancer related pain, and post-operative or injuries after an accident, benefit from the expertise that a pain specialist can offer.

An interventional pain anesthesiologist should be double board certified in both anesthesiology and pain management. This extra training provides these doctors with a highly specialized understanding of the diagnosis and treatment of disorders that cause all types of pain.
Interventional Pain specialists can treat all levels of pain through minimally invasive techniques such as injection therapy, radiofrequency ablation or spinal cord stimulation. They provide treatments such as epidural steroid injections, nerve blocks, radiofrequency ablation, spinal cord stimulation, facet joint injections, lumbar sympathetic plexus blocks, and trigger joint injections. All procedures are done on an outpatient basis.
COMMON PROCEDURE OPTIONS
 Call Today
Call Today
(973) 483-2277
Interventional pain management specialists treat symptoms closely related to chronic pain. These can range from discomfort, difficulty sleeping, soreness, and tightness, to burning, aching, or electrical feelings. Treatments can help relieve pain related to Parkinson’s disease, epilepsy, neuropathy, headaches, bone pain, back pain, and muscle pain. The main areas looked at by Interventional pain physicians are as follows: General Body, Head, Neck and Spine, Hip, Leg and Spine, and Shoulder. Some of the most common procedure options include:
> Adhesiolysis
> Axillary Brachial Plexus Block
> Brachial Plexus Block
> Caudal Steroid Injection
> Celiac Plexus Block
> Cervical Facet Radiofrequency Neurotomy
> Cervical Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injection
> Discography
> Epidural Steroid Injections
> Facet Joint Injections
> Femoral Nerve Block
> Fluoroscopic Guided Hip Injection
> Intracapsular (Glenoid) Injection
> Intrathecal Infusion Devices
> Intrathecal Pump Implant
> Joint Injections
> Lumbar Radiofrequency Neurotomy
> Lumbar Sympathetic Block
> Lumbar Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injection
> Lysis of Adhesions
> Medial Branch Block
> Medication Management
> Necleoplasty
> Nerve Blocks
> Occipital Nerve Block
> Patient-Controlled Analgesia (PCA)
> Peripheral Nerve Block (Ilioinguinal, etc)
> Pulsed Redio Frequency Sympathectomy
> Radiofrequency Lesionings
> Rhizotomy
> Sacroiliac Joint Steroid Injection
> Sciatic Nerve Block
> Spinal Cord Stimulator Implant
> Stellate Ganglion Block
> Suprascapular Nerve Block
> Sympathetic Blocks
> Tailbone/Coccyx Injection
> Thoracic Facet Radiofrequency Neurotomy
> Thoracic Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injection
> Trigger Point Injections
> Vertebroplasty
ABOUT PHYSICAL MEDICINE AND REHABILITATION
Physical medicine and rehabilitation (PM&R;), also called physiatry, is the branch of medicine emphasizing the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of disorders. It is particularly related to disorders of the nerves, muscles, bones and brain that may produce temporary or permanent impairment. PM&R; is one of 24 medical specialties certified by the American Board of Medical Specialties.
Physiatrists, or rehabilitation physicians, are medical doctors who have completed training in the medical specialty of PM&R. Specifically, rehabilitation physicians:
> Diagnose and treat pain
> Restore maximum function lost through injury, illness or disabling conditions
> Treat the whole person, not just the problem area
> Lead a team of medical professionals
> Provide non-surgical treatments
> Explain your medical problems and treatment/prevention plan
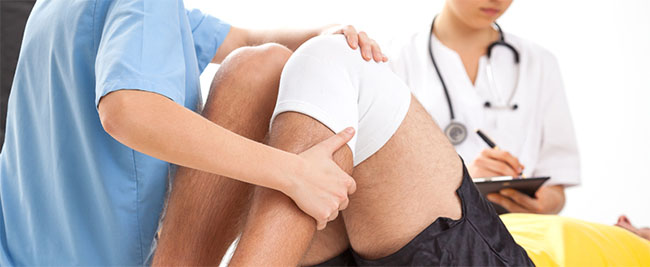
What do Rehabilitation Physicians do?
The job of a rehabilitation physician is to treat any disability resulting from disease or injury, from sore shoulders to spinal cord injuries. The focus is on the development of a comprehensive program for putting the pieces of a person’s life back together after injury or disease – without surgery.
Rehabilitation physicians treat injuries or illnesses that affect how you move, with the aim of enhancing performance. These specialists treat any disability resulting from disease or injury involving any organ system. The focus is not on one part of the body, but instead on the development of a comprehensive program for putting the pieces of a person’s life back together – medically, socially, emotionally, and vocationally – after injury or disease.
Rehabilitation physicians manage issues that span the entire spectrum, from complicated multiple trauma to injury prevention for athletes. They take the time needed to accurately pinpoint the source of an ailment. Then, they design a treatment plan that can be carried out by the patients themselves or with the help of the rehabilitation physician’s medical team.
This medical team might include other physicians and health professionals, such as orthopedic surgeons and physical therapists. By providing an appropriate treatment plan, rehabilitation physicians help patients stay as active as possible at any age. Their broad medical expertise allows them to treat disabling conditions throughout a person’s lifetime.
Spine (Neck and Back)
Treatment for any neck condition is recommended as soon as possible to minimize the danger of further aggravation. There are very broad and general approaches to the treatment of neck pain. The physiatrist at Suburban Orthopaedic Medical Center will develop an individual treatment plan for you.
Low back pain is the most common form of physical disability. An estimated 80 percent of all Americans will suffer from back pain at some point in their lives. Back pain is the second leading cause of work absenteeism. Studies show that early aggressive treatment of back injuries by a physiatrist results in quicker recovery and fewer lost work days. Treatment by physiatrists centers around various combinations of exercise and medication.
> Cervicogenic muscular tension headache
> Occipital neuralgia
> Herniated disc (neck/back)
> Radiculopathy (pinched nerve)
> Discogenic pain
> Degenerative disc disease
> Spondylolysis
> Spondylolisthesis
> Spinal stenosis
> Cervical/thoracic myelopathy
> Postlaminectomy/failed back syndrome
> Low back pain during pregnancy
> Burners/stingers
> Stress fractures/pars defects
> Facet syndrome/arthropathy
SERVICE AREAS AND SYMPTOMS
 Call Today
Call Today
(973) 483-2277
At Suburban Orthopaedic Medical Center in Newark, New Jersey, our Physiatrists treat all injuries of the Spine (Neck and Back), Shoulder, Upper Limb, Elbow, Forearm / Wrist / Hand, Hip / Pelvis, Knee, Lower Leg / Ankle / Foot, including, but not limited to the following:
> Amputations/Prosthetics
> Arthritis Treatment
> Osteoarthritis
> Rheumatoid Arthritis
> Back Pain
> Brain Injuries
> Cardiac Rehabilitation
> Geriatric Rehabilitation
> Neck Pain
> Nerve Pain
> Radiculopathy
> Ulnar Neuropathy (Wrist Pain in Bicyclists)
> Osteoporosis
> Pediatric Rehabilitation
> Post-Polio Syndrome
> Spinal Cord Injuries
> Sports-Related Injuries
> Stroke
> Women’s Conditions
> Female Athlete Triad
> Pelvic Pain
> Pregnancy and Back Pain
> Work-Related Injuries
ABOUT PHYSICAL THERAPISTS
Physical therapists (PTs) at Suburban Orthopaedic Medical Center in Newark, NJ, are highly-educated, licensed health care professionals who can help patients reduce pain and improve or restore mobility – in many cases without expensive surgery and often reducing the need for long-term use of prescription medications and their side effects.
Physical therapy is a type of treatment you may need when health problems like arthritis or carpal tunnel make it hard to move around and do everyday tasks. It helps you move better and may relieve pain. It also helps improve or restore your physical function and your fitness level.
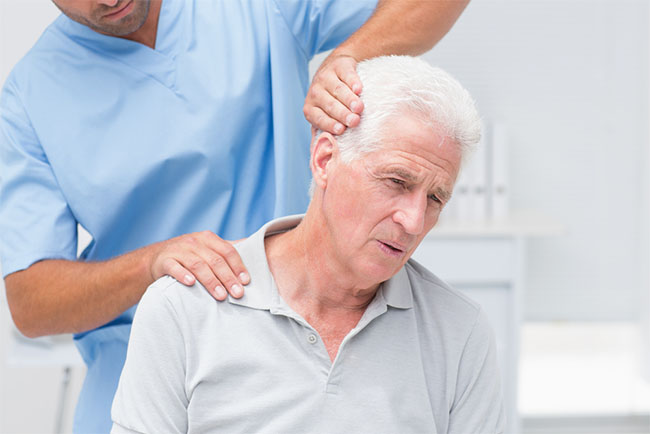
The goal of physical therapy is to make daily tasks and activities easier. For example, it may help with walking, going up stairs, or getting in and out of bed.
Physical therapists can teach patients how to prevent or manage their condition so that they will achieve long-term health benefits. PTs examine each individual and develop a plan, using treatment techniques to promote the ability to move, reduce pain, restore function, and prevent disability. In addition, PTs work with individuals to prevent the loss of mobility before it occurs by developing fitness- and wellness-oriented programs for healthier and more active lifestyles.
Physical therapy can help with recovery after some surgeries. Your doctor may suggest physical therapy for injuries or long-term health problems such as arthritis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Physical therapy may be used alone or with other treatments.
What does a physical therapist do?
Physical therapists provide care for people in a variety of settings, including hospitals, private practices, outpatient clinics, home health agencies, schools, sports and fitness facilities, work settings, and nursing homes. A State license is required in each state in which a physical therapist practices.
Your physical therapist will examine you and talk to you about your symptoms and your daily activity. He or she will then work with you on a treatment plan. The goals are to help your joints move better and to restore or increase your flexibility, strength, endurance, coordination, and/or balance.
First, your therapist will try to reduce your pain and swelling. Your physical therapist also may use manual therapy, education, and techniques such as heat, cold, water, ultrasound, and electrical stimulation. Treatment may cause mild soreness or swelling. This is normal, but talk to your physical therapist if it bothers you.
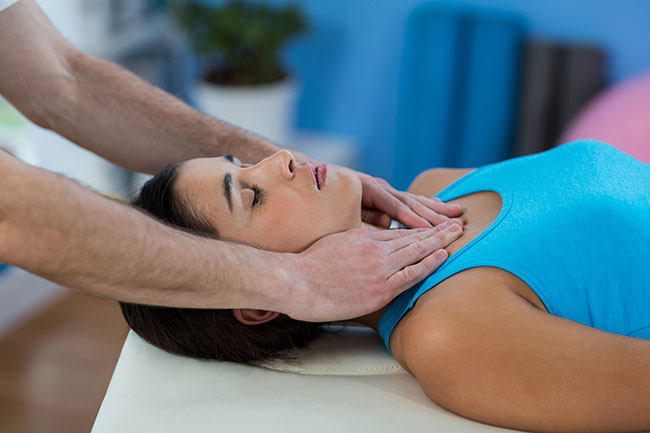
Physical therapy almost always includes exercise. It can include stretching, core exercises, weight lifting, and walking. Your physical therapist may teach you an exercise program so you can do it at home.
Physical Therapist are trained on a broad spectrum and may treat a number of different diagnoses. During you PT session the therapist may test a number of different areas of the body with a significant range of testing. Since Physical Therapists may work on almost any part of the body, these tests may include but are not limited to:
> Aerobic capacity/endurance
> Anthropometric characteristics
> Arousal, attention, and cognition
> Assistive and adaptive devices
> Circulation (arterial, venous, lymphatic)
> Cranial and peripheral nerve integrity
> Environmental, home, and work (job/school/play) barriers
> Ergonomics and body mechanics
> Gait, locomotion, and balance
> Integumentary integrity
> Joint integrity and mobility
> Motor function (motor control and motor learning)
> Muscle performance (including strength, power, and endurance)
> Neuromotor development and sensory integration
> Orthotic, protective, and supportive devices
> Pain
> Posture
> Prosthetic requirements
> Range of motion (including muscle length)
> Reflex integrity
> Self-care and home management (including activities of daily living and instrumental activities of daily living)
> Sensory integrity
> Ventilation, and respiration/gas exchange
> Work (job/school/play), community, leisure integration or reintegration (including instrumental activities of daily living)
SERVICE AREAS AND SYMPTOMS
Call Today
(973) 483-2277
By assessing each individual patient and creating a personalized plan and set of goals the Physical Therapist may perform any of the following, dependent on the individual’s plan of care; keeping in mind the therapist may perform few or many of the following:
> Coordination, communication and documentation
> Patient/client-related instruction
> Therapeutic exercise
> Functional training in self-care and home management (including activities of daily living and instrumental activities of daily living)
> Functional training in work (job/school/play) and community and leisure integration or reintegration activities (including instrumental activities of daily living, work hardening, and work conditioning)
> Manual therapy techniques (including mobilization/manipulation)
> Prescription, application, and, as appropriate, fabrication of devices and equipment (assistive, adaptive, orthotic, protective, supportive, and prosthetic)
> Airway clearance techniques
> Integumentary repair and protection techniques
> Electrotherapeutic modalities
> Physical agents and mechanical modalities
> Dry needling
ABOUT ORTHOPAEDICS
Orthopedics is the medical specialty that focuses on injuries and diseases of your body’s musculoskeletal system. This complex system includes your bones, joints, ligaments, tendons, muscles, and nerves and allows you to move, work, and be active.
Once devoted to the care of children with spine and limb deformities, orthopedists now care for patients of all ages, from newborns with clubfeet to young athletes requiring arthroscopic surgery to older people with arthritis. And anybody can break a bone.

Orthopedics surgeons manage special problems of the musculoskeletal system. This involves:
> Diagnosis of your injury or disorder.
> Treatment with medication, exercise, surgery or other treatment plans.
> Rehabilitation by recommending exercises or physical therapy to restore movement, strength and function.
> Prevention with information and treatment plans to prevent injury or slow the progression of diseases.
While orthopedic surgeons are familiar with all aspects of the musculoskeletal system, many orthopaedists specialize in certain areas, such as the foot and ankle, spine, hip or knee. They may also choose to focus on specific fields like pediatrics, trauma or sports medicine. Some orthopedic surgeons may specialize in several areas.
Education and Training
Your orthopedic surgeon is a medical doctor with extensive training in the proper diagnosis and treatment of injuries and diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Your orthopedic surgeons completed up to 14 years of formal education.
> Four years of study in a college or university.
> Four years of study in medical school.
> Five years of study in orthopedic residency at a major medical center.
> One optional year of specialized education.
After establishing a licensed practice, your orthopedic surgeon demonstrated mastery of orthopedic knowledge by passing both oral and written examinations given by the American Board of Orthopaedic Surgery.
Each year your orthopaedic surgeon spends many hours studying and attending continuing medical education courses to stay up-to-date in current orthopedic knowledge and skills.
Treatment
Orthopaedic surgeons treat many musculoskeletal conditions without surgery, by using medication, exercise and other rehabilitative or alternative therapies. For most orthopedic diseases and injuries there is more than one form of treatment. If necessary, he/she may also recommend surgery if you do not respond to other treatments.
Your Doctor’s Visit
Your visit will start with a personal interview and physical examination. This may be followed by diagnostic tests such as blood tests, X-rays, or other tests.
Your orthopaedic surgeon will discuss your diagnosis and available treatment options with you and help you select the proper treatment plan.
IMAGING SERVICES
 Call Today
Call Today
(973) 483-2277
The following imaging services are available at Suburban Orthopaedic Medical Center:
> Digital X-Ray
> MRI
> Fluoroscopy
> Diagnostic Ultrasound
> Interventional Ultrasound
ORTHOPEDIC INJURY TREATMENTS AND CONDITIONS
> Hand, Wrist, Elbow
> Shoulder
> Neck & Spine
> Hip & Knee
> Foot & Ankle
> Pediatrics
> Sports Medicine
> Joint Replacement
> Pain Management
> Arthritis (disease of the joints) and Joint Replacement: joint pain, total hip replacement, total knee replacement
> Osteoarthritis (the most common type of arthritis, where cartilage in your joints wears down over time): diseases affecting the joints including rheumatoid arthritis.
> Elbow Care: Surgery for tennis elbow and other athletic elbow injuries, arthritis and inflammatory joint abnormalities, arthroscopic elbow surgery, elbow replacement surgery, elbow bracing.
> Foot and Ankle/Podiatry: Care for bunions (abnormal growths at the base of your big toe), hammertoes (toes that curl up at the joint), diabetic foot care, heel pain, fractures, and sports injuries.
> Hand and Upper Extremity: Surgical and non-surgical treatment for hand, wrist, elbow, and shoulder conditions, such as carpal tunnel and hand fractures/trauma.
> Orthopedic Oncology (Bone Cancer): Care for Ewing’s sarcoma, osteosarcoma, and other tumors affecting bones and supporting muscles.
> Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation (Physiatry): Non-surgical treatment for back pain, including physical, occupational and speech therapy management.
> Rheumatology: Treatment of arthritis and other diseases of the joints and muscles.
> Shoulder Care: Treatments for shoulder muscle, joint pain, and shoulder injury including rotator cuff surgery, arthroscopic shoulder surgery, shoulder joint replacement.
> Spine care: Including surgical and non-surgical treatments for back pain, sciatica, herniated discs, spine injuries, spinal stenosis, osteoporosis, deformities and arthritis and whiplash.
> Sports Medicine: Arthroscopic and reconstructive surgery and nonsurgical treatments for sports related injuries, including tennis elbow, ACL tears, and other knee injuries, repetitive and overuse injuries, back injuries, dislocations, fractures, and ligament damage.
> Fracture and Orthopedics: Emergency care for acute traumatic injuries, such as fractures and crush injuries.
> Concussion Care: Immediate care and follow-up care for concussion related injuries.