Continuous turning and twisting can take a toll on the neck and back. Blame it on everything from overuse of technology, or on increasingly hectic lifestyle, to a deteriorating diet. The truth is that an estimated two out of three individuals experience neck or back pain at some point in their lives. One of the biggest causes of neck and lower back pain is a degenerated disc. Degenerative disc disease is quite common in older people, and its effects vary in nature and severity.
The participating physician members of Suburban Orthopaedic Medical Center offer various treatment options for a multitude of spinal conditions including Degenerative Disc Disease. The following blog is a summary of the disorder, including causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment.
Symptoms of Degenerative Disc Disease
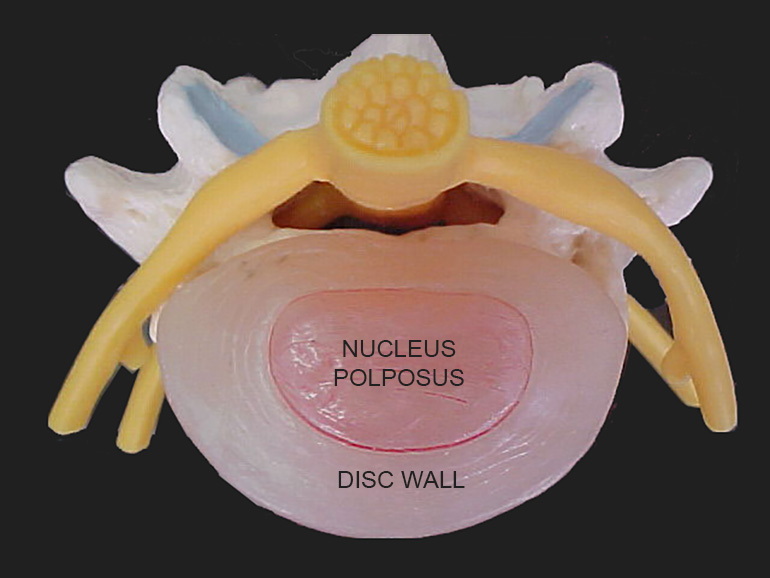
Degenerative Disc Disease is a weakening of one or more vertebral discs, which normally act as a cushion between the vertebrae. This condition can develop as a part of the aging process, but it may also result from injury to the back. Degenerative Disc Disease commonly begins when small tears appear in the disc wall, called the annulus. These tears can cause pain. When the tears heal, creating scar tissue that is not as strong as the original disc wall. If the back is repeatedly injured, the process of tearing and scarring may continue. This will ultimately result in the weakening of the disc wall. Over a period of time, the center (or nucleus) of the disc becomes damaged and loses some of its water content. This center is called the pulposus. Its water content is needed to keep the disc functioning as a shock absorber for the spine.
Unable to act as a cushion, the nucleus collapses. The vertebrae above and below this damaged disc slide closer together. This improper alignment causes facet joints – the areas where the vertebral bones touch – to twist into an unnatural position. In time, this awkward positioning of the vertebrae may create bone spurs. If these spurs grow into the spinal canal, they may pinch the spinal cord and nerves (a condition called spinal stenosis). The site of the injury may be painful. Many people experience pain, numbness, or tingling in the legs. Strong pain tends to come and go. Bending, twisting and sitting may make the pain worse. Lying down tends to relieve pressure on the spine.
Diagnose
To diagnose degenerative disc disease, doctors take into account many factors. These include the medical history of the patient, the intensity of the problem, and the factors that improve or worsen the condition. Often, neurological examinations help in testing the muscle strength, reflexes and sensation in the arms and hands. Imaging tests, like the MRI, X-rays and CT scan enable physicians to visualize the spine and connect the source of the pain or stiffness to the severity of the problem. Based on the findings, the physician will prescribe a suitable course of treatment.

Treatment
The treatment for degenerative disc disease is typically a combination of three steps: Pain Control; Exercise and Physical Therapy; and Lifestyle Changes. Regular exercise helps in healing the damaged disc, and also prevents or reduces the recurrence of the pain. It is essential for people with symptomatic Degenerative Disc Disease to exercise under the guidance of a physical therapist or a trained healthcare professional. In addition, it is vital to develop a healthy lifestyle. Patients must avoid nicotine, alcohol abuse, and staying in one position for too long. On the up side, drinking plenty of water and gentle hamstring stretching can help to relieve the pain.
Conclusion
Degenerative disc disease, if diagnosed at an early stage, can be treated without surgery. In these cases, physicians may prescribe over-the-counter drugs and physiotherapy to treat the problem. If the pain persists for more than a few months even after resorting to primary treatments, doctors may recommend pain management and surgical options. If you experience pain or stiffness in the neck or back, seek a consultation from a physician. The participating physician members at Suburban Orthopaedic Medical Center specialize in the treatment of degenerative disc disease and other spinal and orthopaedic disorders. To make an appointment, call us now at (973) 483-2277.
Share this article:


